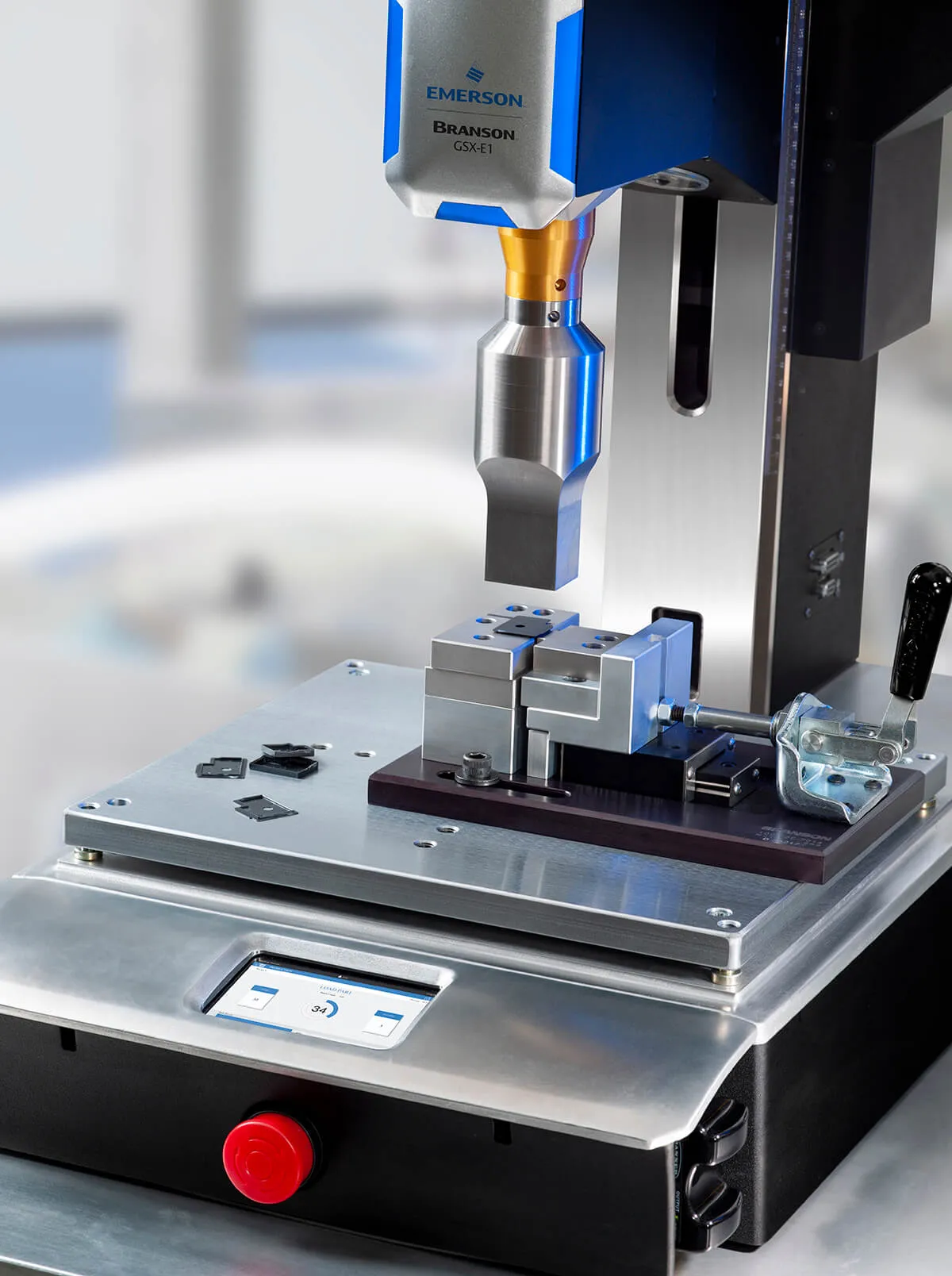
Ultrasonic welding is an advanced technology widely used in precision machining. This method does not require any filler materials but instead relies on ultrasonic vibrations to bond metal or plastic surfaces together. Ultrasonic welding is increasingly applied across various industries, especially in fields that demand high precision.
So, what are the specific applications of this method in the precision engineering industry, and in which sectors is it commonly used? Let’s explore the answers with PWP Solution in the article below!
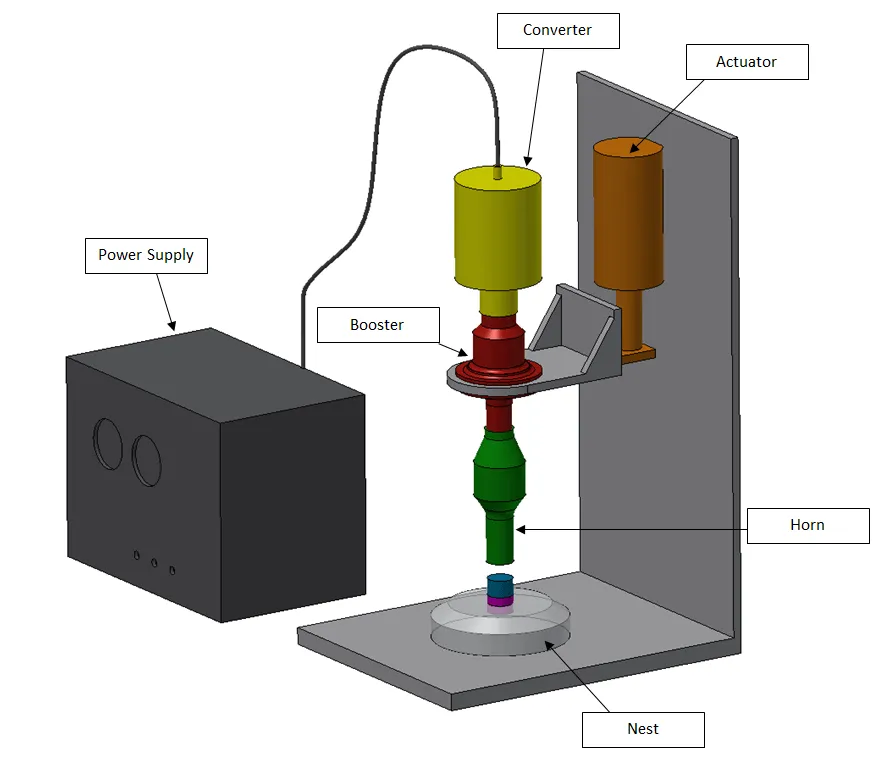
Ultrasonic welding operates based on the principle of high-frequency mechanical vibrations. When two material surfaces come into contact, the ultrasonic welding head generates sound waves with frequencies ranging from 15 kHz to 70 kHz. The friction between the surfaces causes localized melting of the materials, allowing them to bond together without the need for adhesives or high temperatures as required by traditional welding methods.
Compared to other welding methods, ultrasonic welding offers numerous outstanding features and greater efficiency, such as:
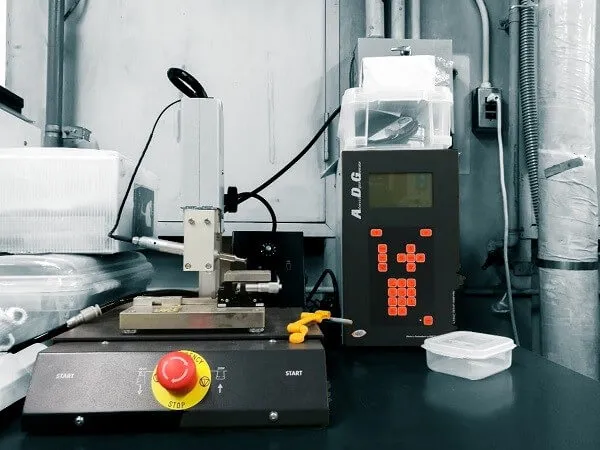

Fast welding speed with no cooling time required, improving production efficiency.
No need for additional welding materials, reducing production costs and avoiding product contamination.
High precision, with no effect on the structure or properties of the materials.
Environmentally friendly, producing no smoke, sparks, or hazardous waste.
High stability, ensuring strong and durable weld joints.
Ultrasonic welding is increasingly adopted by businesses looking to invest in automation and enhance product quality. It is widely used in various industries, including:
Ultrasonic welding enables the precise connection of small electronic components without damage caused by high temperatures, unlike traditional methods. Common applications include:
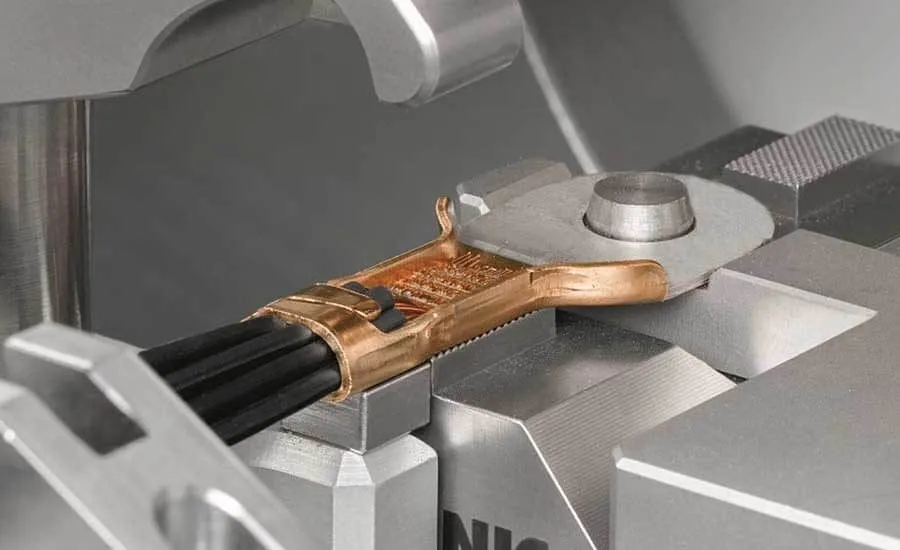

Welding wires and cables onto circuit boards.
Welding microchips and mini sensors in modern electronic devices.
Ultrasonic welding is used to assemble small parts in medical devices, ensuring sterility and high precision. Specific applications include:
Welding plastic components in syringes and surgical tools.
Welding microchips in implants and pacemakers.
In the manufacturing of measuring instruments, this technology helps join small components without affecting material quality. Applications include:

Welding tiny parts in measuring instruments and gauges.
Connecting components in microscopes and optical equipment.
Ultrasonic welding is used in the production of microfluidic devices for medical and biological research, helping bond microchannels without affecting their function. Some applications include:

Manufacturing microfluidic chips for medical diagnostics.
Welding ultra-small tubes for biological analysis.
This technology supports the production of lightweight and durable components, improving performance and reducing product weight. Specific applications include:
Welding car frame parts to reduce vehicle weight and increase fuel efficiency.
Welding metal and composite components in aerospace to improve durability and reduce maintenance costs.
Ultrasonic welding is an effective solution for precision machining, improving product quality, reducing costs, and protecting the environment. As a non-destructive welding method, it not only ensures a clean finish but also preserves the necessary functions of the product. In the near future, ultrasonic welding will continue to develop and become especially prevalent in fields requiring high precision and sustainability to achieve the highest efficiency. If you're unsure whether your product is suitable for ultrasonic welding, don’t hesitate to contact PWP Solution for the fastest and most accurate consultation!

